Prerequisite - You will need these tools
- Vagrant
- PostgreSQL
- Postman
Deploy module on Vagrant
- Thunderjet - Onboarding plan
- How to run folio backend modules with IntelliJ Idea and interact with Vagrant box environment
- Vagrantfile (use this file as an example. it includes Kafka port, PostgreSQL port and some extra functionalities which help vagrant works smoothly)
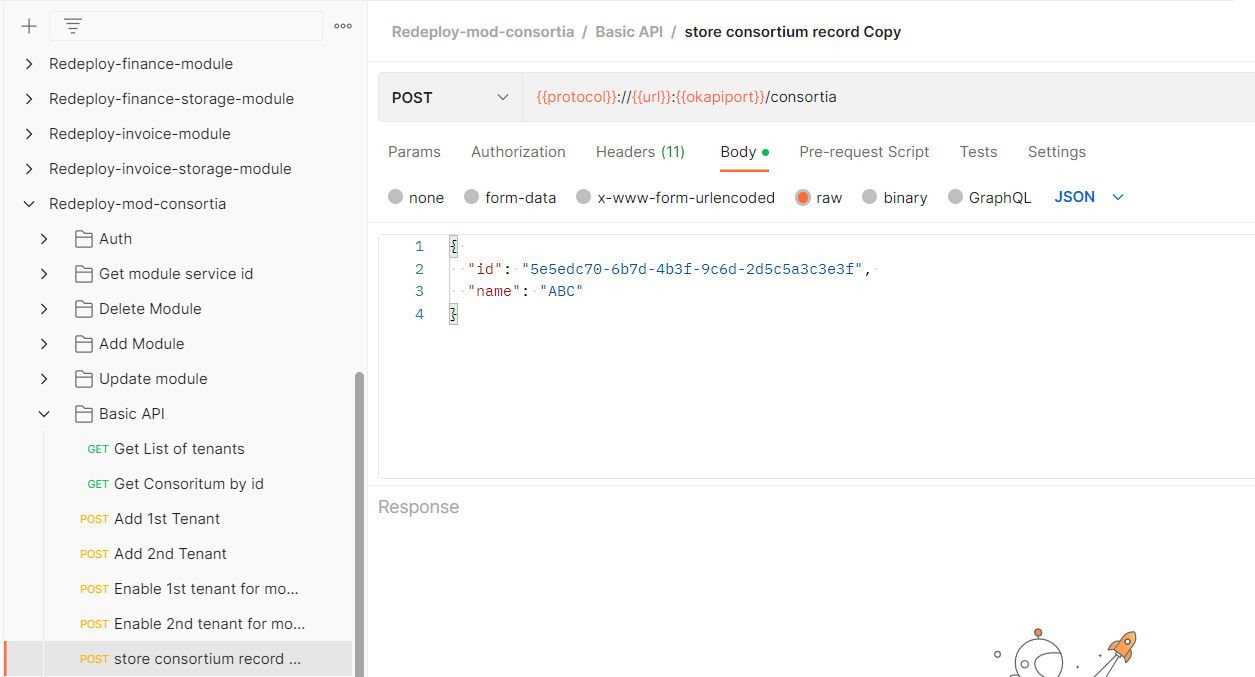
- Postman Collection for Mod-Consortia (it include all basic API request) - Redeploy-mod-consortia.postman_collection.json
Result:
default port 8081 for mod-consortia. your requests from postman collection (get list of tenant request) works expected
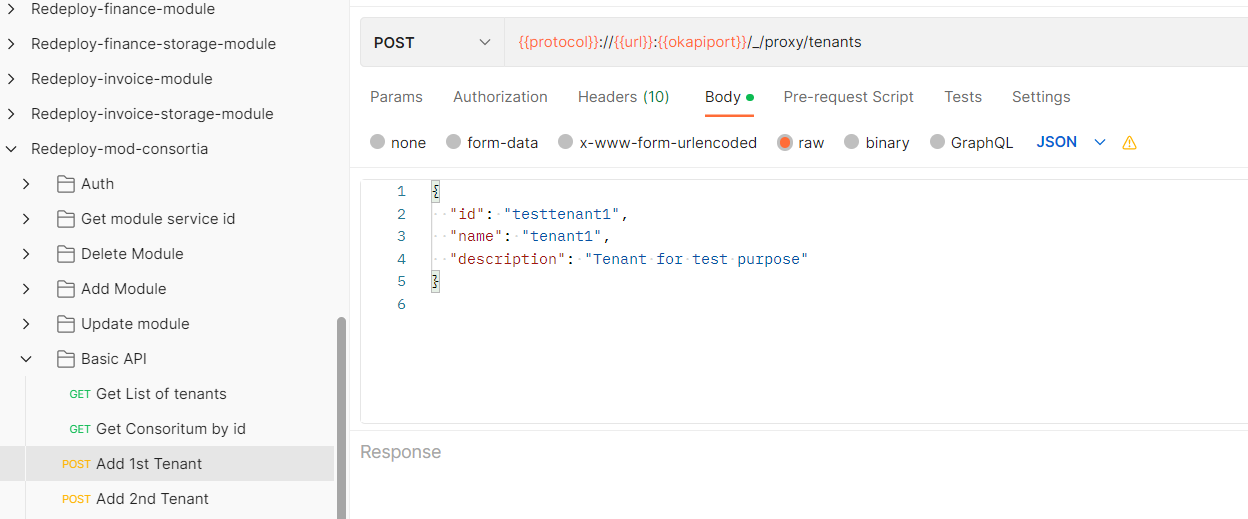
Create a tenant locally
If everything is working well until this step, Let's move on to creating tenants locally.
Theory:
Before creating a tenant, we need to understand what creating a tenant locally
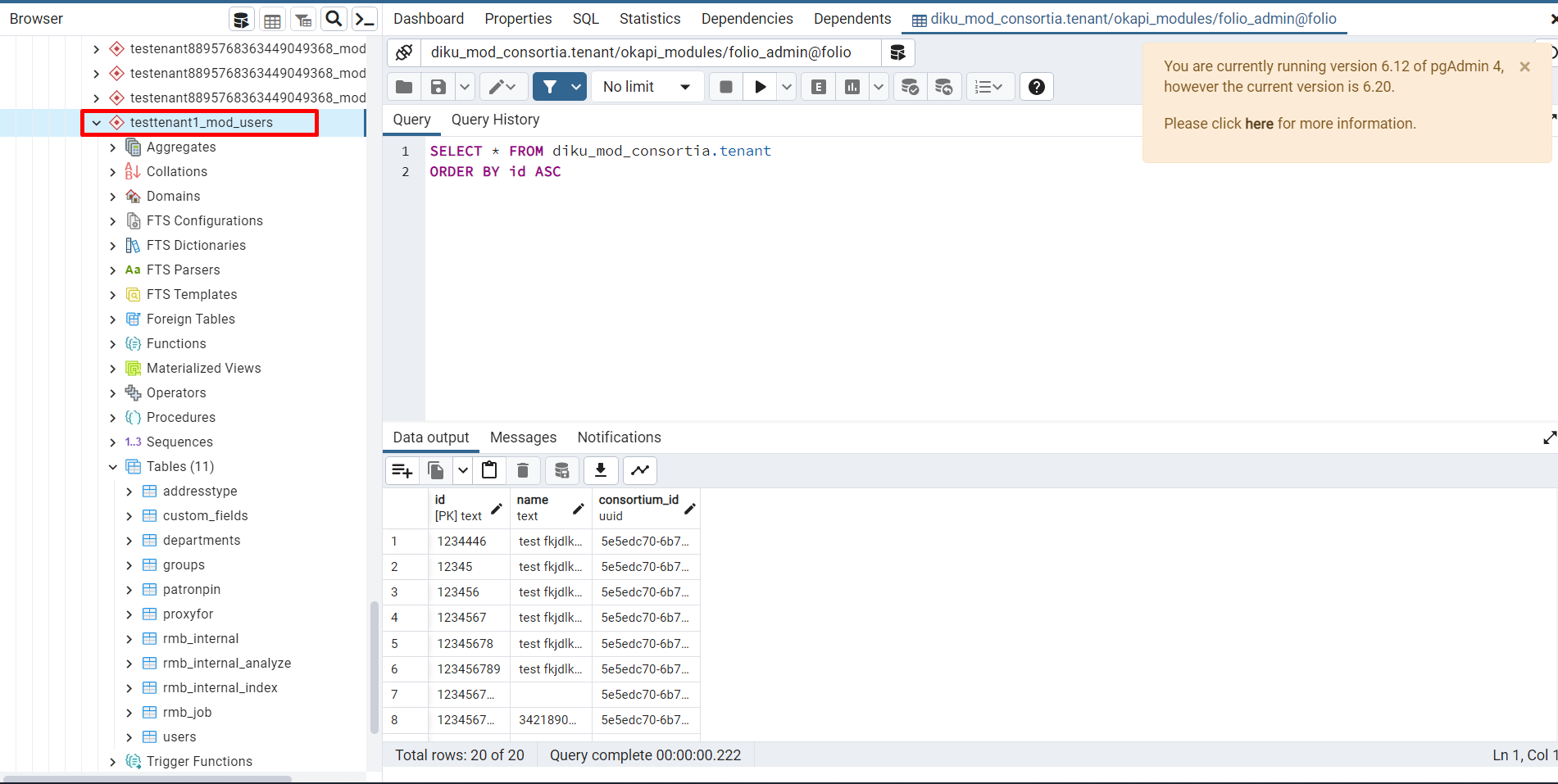
If we create a new tenant, we will create schemas for this tenant.
These are tenants. if we enable the module for the tenant, it will create a new schema for this tenant
For example
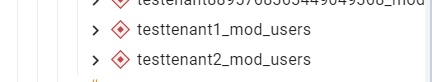
- we created testtenant1
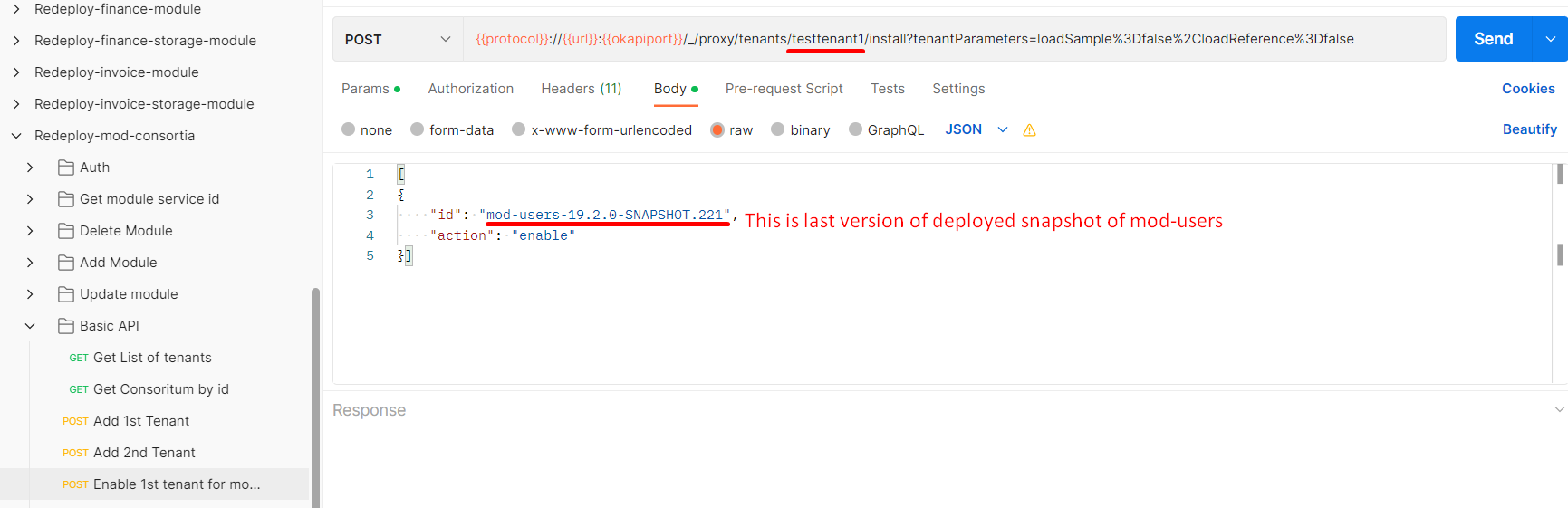
- enabled mod-user(mod-users-19.2.0-SNAPSHOT.221)
- new schema testtenant1_mod_user created inside Schemas
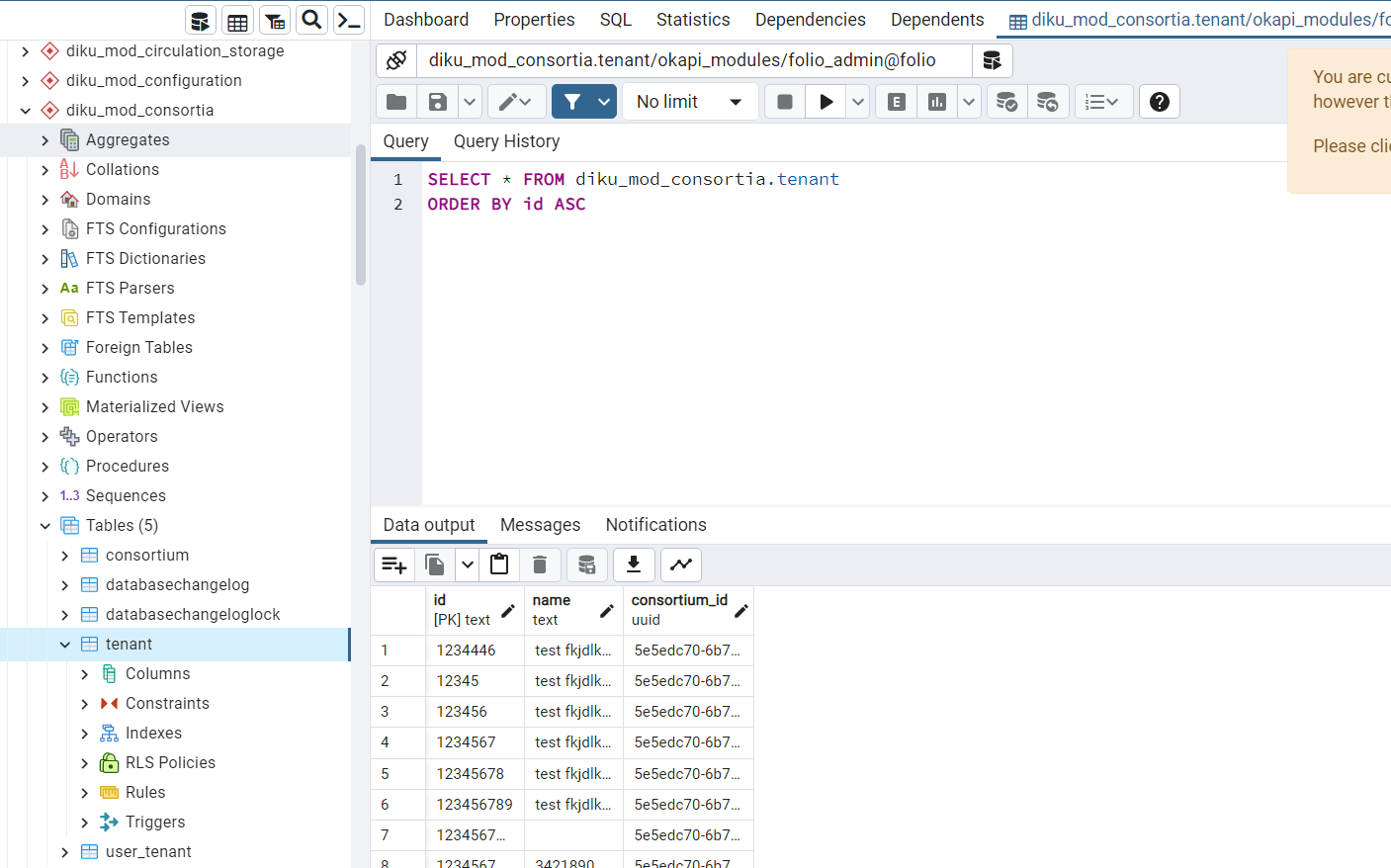
Mod-consortia stores tenant information inside the tenant table
Process:
- create consortium (it will be only one consortium)
- create tenant
- enable tenant for module (mod_users)
New schema will be created (testtenant1_mod_user → testtenant1 - tenant name, mod_user - enabled module)