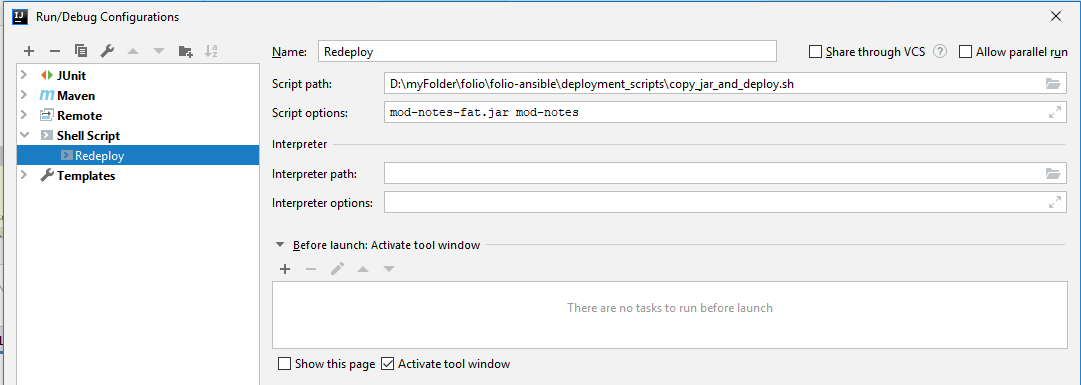
This guide is based on How to automate new modules’ registration within folio/testing-backend Vagrant box. It provides shell scripts for re-registering/redeploying modules in folio/testing Vagrant box.
The goal is to set up a script that will be run after module is built. The script will copy all necessary files, build docker image, register and deploy it inside of Vagrant box.
This guide assumes that Okapi already has a version of the same module registered and deployed. The script will only replace old module with new one, it won't register module from scratch.
Additionally version of new module has to be greater or equal to the version of already deployed module
Related articles