What is Codex?
...
But in practice, domains, and the microservices they contain, form a system and there are necessary interactions between the microservices, including across domain boundaries. Those interactions create dependencies, and in a flat model, this leads to entanglement - thus breaking the promise of a loosely coupled system.
The Entanglement Problem
The interaction between microservices (i.e. modules) is an integration problem. It requires that individual modules be aware of other modules. For modules in the same domain, this is expected and not an issue. However, the same is not true across domain boundaries.
...
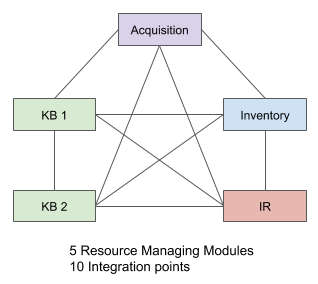
This may seem like a manageable approach that can scale linearly. But it is not. Now imagine that a Folio system has 5 resource managing modules. In all likelihood, in a flat modular system, each module will likely need to be aware of each of the other 4. As shown below, the number of interdependencies grows to 10.
<IMAGE: DEPENDENCIES 3>
In the general case, if a Folio system has N resource managing modules, the number of potential integration points isN(N-1)/2, which is not linear, but scales on the order of N2.
...
Codex is a hierarchical domain that acts as a coordinator for resource management. As a coordination domain it is Codex’s business to know about the other domains.
A Hierarchical Domain Model
A significant responsibility of Folio is to manage resources, and more specifically the records that describe those resources. However, not all parts of Folio require the same level of detail for those resources. Nor do they have the same scope requirements: Circulation doesn’t much care about the purchase price of an item, but Acquisitions certainly does. The following diagram focuses on resource management specifically. As shown, the resource managing domains can be organized into layers based on the depth of detail that they require and the purpose they serve.
...